| lab | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Lab: Implement and Manage Storage
All tasks in this lab are performed from the Azure portal (including a PowerShell Cloud Shell session) except for Exercise 2 Task 2, which includes steps performed from a Remote Desktop session to an Azure VM
Note: When not using Cloud Shell, the lab virtual machine must have the Azure PowerShell 1.2.0 module (or newer) installed https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/azure/install-az-ps
Lab files:
- Labfiles\Module_03\Implement_and_Manage_Storage\az-100-02_azuredeploy.json
- Labfiles\Module_03\Implement_and_Manage_Storage\az-100-02_azuredeploy.parameters.json
Scenario
Adatum Corporation wants to leverage Azure Storage for hosting its data
Objectives
After completing this lab, you will be able to:
- Deploy an Azure VM by using an Azure Resource Manager template
- Implement and use Azure Blob Storage
- Implement and use Azure File Storage
Exercise 0: Prepare the lab environment
The main tasks for this exercise are as follows:
- Deploy an Azure VM by using an Azure Resource Manager template
Task 1: Deploy an Azure VM by using an Azure Resource Manager template
- From the lab virtual machine, start Microsoft Edge, browse to the Azure portal at http://portal.azure.com and sign in by using a Microsoft account that has the Owner role in the Azure subscription you intend to use in this lab.
- In the Azure portal, navigate to the Subscriptions blade.
- From the Subscriptions blade, navigate to the blade displaying properties of your Azure subscription.
- From the blade displaying the properties of your subscription, navigate to its Resource providers blade.
- On the Resource providers blade, register the following resource providers (if these resource providers have not been yet registered):
- Microsoft.Network
- Microsoft.Compute
- Microsoft.Storage
Note: This step registers the Azure Resource Manager Microsoft.Network, Microsoft.Compute, and Microsoft.Storage resource providers. This is a one-time operation (per subscription) required when using Azure Resource Manager templates to deploy resources managed by these resource providers (if these resource providers have not been yet registered).
- In the Azure portal, navigate to the Create a resource blade.
- From the Create a resource blade, search Azure Marketplace for Template deployment, and select Template deployment (deploy using custom templates)
- Click Create.
- On the Custom deployment blade, click the Build your own template in the editor link. If you do not see this link, click Edit template instead.
- From the Edit template blade, load the template file Labfiles\Module_03\Implement_and_Manage_Storage\az-100-02_azuredeploy.json.Note: Review the content of the template and note that it defines deployment of an Azure VM hosting Windows Server 2016 Datacenter.
- Save the template and return to the Custom deployment blade.
- From the Custom deployment blade, navigate to the Edit parameters blade.
- From the Edit parameters blade, load the parameters file Labfiles\Module_03\Implement_and_Manage_Storage\az-100-02_azuredeploy.parameters.json.
- Save the parameters and return to the Custom deployment blade.
- From the Custom deployment blade, initiate a template deployment with the following settings:
- Subscription: the name of the subscription you are using in this lab
- Resource group: the name of a new resource group az1000201-RG
- Location: the name of the Azure region which is closest to the lab location and where you can provision Azure VMs
- Vm Size: use Standard_DS1_v2 or Standard_DS2_v2, based on the instructor's recommendations
- Vm Name: az1000201-vm1
- Admin Username: Student
- Admin Password: Pa55w.rd1234
- Virtual Network Name: az1000201-vnet1
Note: To identify Azure regions where you can provision Azure VMs, refer to https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/regions/offers/Note: Do not wait for the deployment to complete but proceed to the next exercise. You will use the virtual machine az1000201-vm1 in the second exercise of this lab.
Exercise 1: Implement and use Azure Blob Storage
The main tasks for this exercise are as follows:
- Create Azure Storage accounts
- Review configuration settings of Azure Storage accounts
- Manage Azure Storage Blob Service
- Copy a container and blobs between Azure Storage accounts
- Use a Shared Access Signature (SAS) key to access a blob
Task 1: Create Azure Storage accounts
- In the Azure portal, navigate to the Create a resource blade.
- From the Create a resource blade, search Azure Marketplace for Storage account.
- Use the list of search results to navigate to the Create storage account blade.
- From the Create storage account blade, create a new storage account with the following settings:
- Subscription: the same subscription you selected in the previous task
- Resource group: the name of a new resource group az1000202-RG
- Storage account name: any valid, unique name between 3 and 24 characters consisting of lowercase letters and digits
- Location: the name of the Azure region which you selected in the previous task
- Performance: Standard
- Account kind: Storage (general purpose v1)
- Replication: Locally-redundant storage (LRS)
- Do not wait for the storage account to be provisioned but proceed to the next step.
- In the Azure portal, navigate to the Create a resource blade.
- From the Create a resource blade, search Azure Marketplace for Storage account.
- Use the list of search results to navigate to the Create storage account blade.
- From the Create storage account blade, create a new storage account with the following settings:
- Subscription: the same subscription you selected in the previous task
- Resource group: the name of a new resource group az1000203-RG
- Storage account name: any valid, unique name between 3 and 24 characters consisting of lowercase letters and digits
- Location: the name of an Azure region different from the one you chose when creating the first storage account
- Performance: Standard
- Account kind: StorageV2 (general purpose v2)
- Access tier: Hot
- Replication: Geo-redundant storage (GRS)
- Wait for the storage account to be provisioned. This should take less than a minute.
Task 2: Review configuration settings of Azure Storage accounts
- In Azure Portal, navigate to the blade of the first storage account you created.
- With your storage account blade open, review the storage account configuration in the Overview section, including the performance, replication, and account kind settings.
- Display the Access keys blade. Note that you have the option of copying the values of storage account name, as well as the values of key1 and key2. You also have the option to regenerate each of the keys.
- Display the Configuration blade of the storage account.
- On the Configuration blade, note that you have the option of performing an upgrade to General Purpose v2 account, enforcing secure transfer, and changing the replication settings to either Geo-redundant storage (GRS) or Read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS). However, you cannot change the performance setting (this setting can only be assigned when the storage account is created).
- Display the Encryption blade of the storage account. Note that encryption is enabled by default and that you have the option of using your own key.Note: Do not change the configuration of the storage account.
- In Azure Portal, navigate to the blade of the second storage account you created.
- With your storage account blade open, review the storage account configuration in the Overview section, including the performance, replication, and account kind settings.
- Display the Configuration blade of the storage account.
- On the Configuration blade, note that you have the option of disabling the secure transfer requirement, setting the default access tier to Cool, and changing the replication settings to either Locally-redundant storage (LRS) or Read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS). In this case, you also cannot change the performance setting.
- Display the Encryption blade of the storage account. Note that in this case encryption is also enabled by default and that you have the option of using your own key.
Task 3: Manage Azure Storage Blob Service
- In the Azure portal, navigate to the Containers blade of the first storage account you created.
- From the Containers blade of the first storage account, create a new container named az1000202-container with the Public access level set to Private (no anonymous access).
Task 4: Copy a container and blobs between Azure Storage accounts
- From the Azure Portal, start a PowerShell session in the Cloud Shell pane.Note: If this is the first time you are launching the Cloud Shell in the current Azure subscription, you will be asked to create an Azure file share to persist Cloud Shell files. If so, accept the defaults, which will result in creation of a storage account in an automatically generated resource group.
- In the Cloud Shell pane, run the following commands:
$containerName = 'az1000202-container' $storageAccount1Name = (Get-AzStorageAccount -ResourceGroupName 'az1000202-RG')[0].StorageAccountName $storageAccount2Name = (Get-AzStorageAccount -ResourceGroupName 'az1000203-RG')[0].StorageAccountName $storageAccount1Key1 = (Get-AzStorageAccountKey -ResourceGroupName 'az1000202-RG' -StorageAccountName $storageAccount1Name)[0].Value $storageAccount2Key1 = (Get-AzStorageAccountKey -ResourceGroupName 'az1000203-RG' -StorageAccountName $storageAccount2Name)[0].Value $context1 = New-AzStorageContext -StorageAccountName $storageAccount1Name -StorageAccountKey $storageAccount1Key1 $context2 = New-AzStorageContext -StorageAccountName $storageAccount2Name -StorageAccountKey $storageAccount2Key1
Note: These commands set the values of variables representing the names of the blob container containing the blobs you uploaded in the previous task, the two storage accounts, their corresponding keys, and the corresponding security context for each. You will use these values to generate a SAS token to copy blobs between storage accounts by using the AZCopy command line utility.
- In the Cloud Shell pane, run the following command:
New-AzStorageContainer -Name $containerName -Context $context2 -Permission Off
Note: This command creates a new container with the matching name in the second storage account - In the Cloud Shell pane, run the following commands:
$containerToken1 = New-AzStorageContainerSASToken -Context $context1 -ExpiryTime(get-date).AddHours(24) -FullUri -Name $containerName -Permission rwdl $containerToken2 = New-AzStorageContainerSASToken -Context $context2 -ExpiryTime(get-date).AddHours(24) -FullUri -Name $containerName -Permission rwdl
Note: These commands generate SAS keys that you will use in the next step to copy blobs between two containers. - In the Cloud Shell pane, run the following command:
azcopy cp $containerToken1 $containerToken2 --recursive=true
Note: This command uses the AzCopy utility to copy the content of the container between the two storage accounts. - Verify that the command returned the results confirming that the two files were transferred.
Task 5: Use a Shared Access Signature (SAS) key to access a blob
- From the Containers blade of the second storage account, navigate to the container az1000202-container, and then open the az-100-02_azuredeploy.json blade.
- On the az-100-02_azuredeploy.json blade, copy the value of the URL property.
- Open another Microsoft Edge window and navigate to the URL you copied in the previous step.Note: The browser will display the ResourceNotFound. This is expected since the container has the Public access level set to Private (no anonymous access).
- On the az-100-02_azuredeploy.json blade, generate a shared access signature (SAS) and the corresponding URL with the following settings:
- Permissions: Read
- Start date/time: specify the current date/time in your current time zone
- Expiry date/time: specify the date/time 24 hours ahead of the current time
- Allowed IP addresses: leave blank
- Allowed protocols: HTTP
- Signing key: Key 1
- On the az-100-02_azuredeploy.json blade, copy Blob SAS URL.
- From the previously opened Microsoft Edge window, navigate to the URL you copied in the previous step.Note: This time, you will be prompted whether you want to open or save az-100-02_azuredeploy.json. This is expected as well, since this time you are no longer accessing the container anonymously, but instead you are using the newly generated SAS key, which is valid for the next 24 hours.
- Close the Microsoft Edge window displaying the prompt.
Result: After you completed this exercise, you have created two Azure Storage accounts, reviewed their configuration settings, created a blob container, uploaded blobs into the container, copied the container and blobs between the storage accounts, and used a SAS key to access one of the blobs.
Exercise 2: Implement and use Azure File Storage
The main tasks for this exercise are as follows:
- Create an Azure File Service share
- Map a drive to the Azure File Service share from an Azure VM
Task 1: Create an Azure File Service share
- In the Azure portal, navigate to the blade displaying the properties of the second storage account you created in the previous exercise.
- From the storage account blade select File shares under File Service.
- From the storage account File shares blade, create a new file share with the following settings:
- Name: az10002share1
- Quota: 5 GB
Task 2: Map a drive to the Azure File Service share from an Azure VM
Note: Before you start this task, ensure that the template deployment you started in Exercise 0 has completed.
- Navigate to the az10002share1 blade and display the Connect blade.
- From the Connect blade, copy into Clipboard the PowerShell commands that connect to the file share from a Windows computer.
- In the Azure portal, navigate to the az1000201-vm1 blade.
- From the az1000201-vm1 blade, connect to the Azure VM via the RDP protocol and, when prompted to sign in, provide the following credentials:
- Admin Username: Student
- Admin Password: Pa55w.rd1234
- From the Windows PowerShell ISE session, open the script pane and paste into it the content of your local Clipboard.
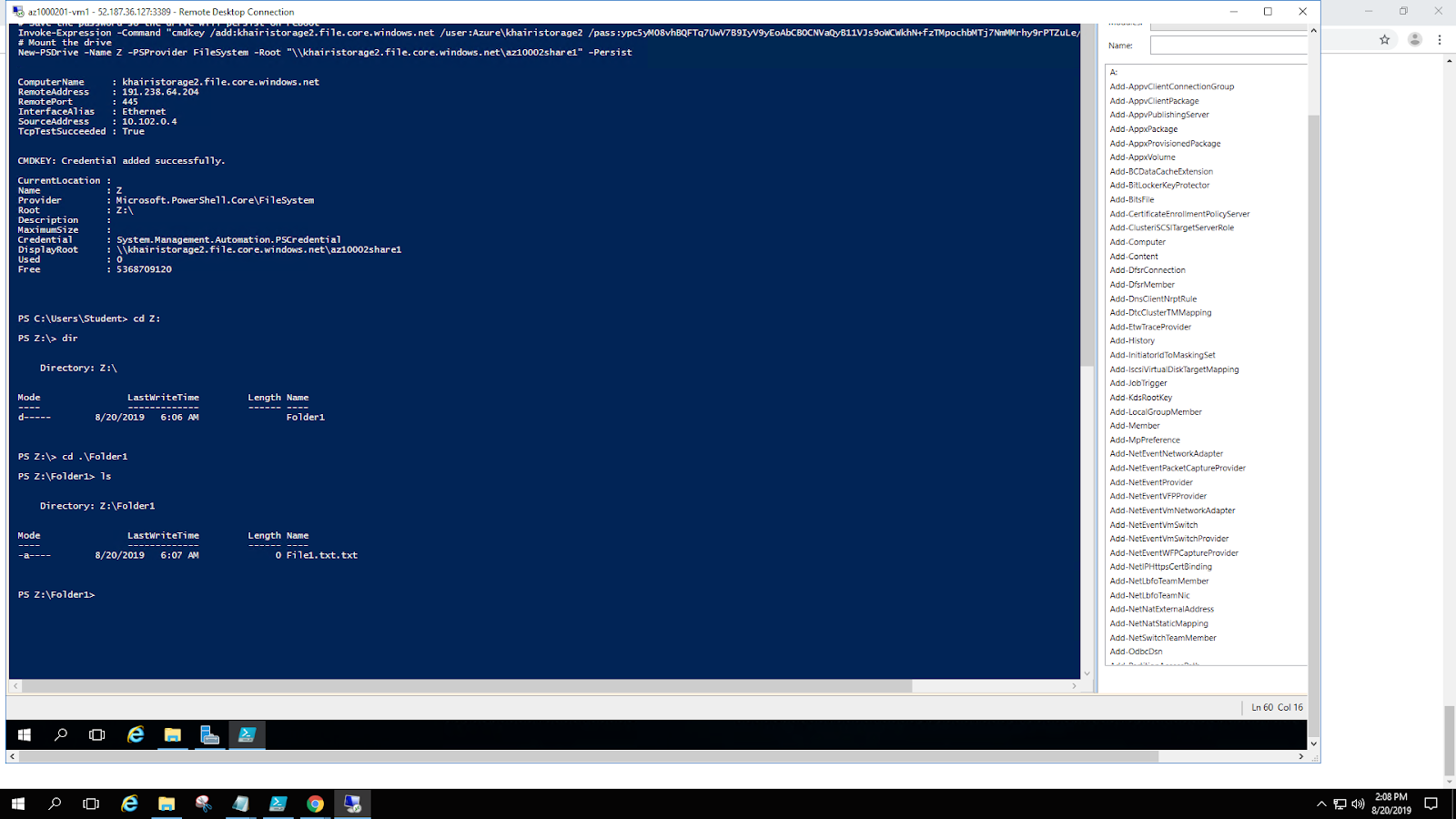
- In the File Explorer window, create a folder named Folder1 on the Z: drive.
- In the File Explorer window, navigate to Folder1 and create a text document named File1.txt.Note: Make sure that you take into account the default configuration of File Explorer that does not display known file extensions in order to avoid creating a file named File1.txt.txt.
- From the PowerShell prompt, enter Z: to change the directory context to the mapped drive.
- From the PowerShell prompt, enter dir to list the contents of the drive. You should see the directory that you created from File Explorer.
- From the PowerShell prompt, enter cd Folder1 to change directories to the folder. Run the dir command again to list the file contents.
Exercise 3: Remove lab resources
Task 1: Open Cloud Shell
- At the top of the portal, click the Cloud Shell icon to open the Cloud Shell pane.
- At the Cloud Shell interface, select Bash.
- At the Cloud Shell command prompt, type in the following command and press Enter to list all resource groups you created in this lab:
az group list --query "[?starts_with(name,'az1000')].name" --output tsv - Verify that the output contains only the resource groups you created in this lab. These groups will be deleted in the next task.
Task 2: Delete resource groups
- At the Cloud Shell command prompt, type in the following command and press Enter to delete the resource groups you created in this lab
az group list --query "[?starts_with(name,'az1000')].name" --output tsv | xargs -L1 bash -c 'az group delete --name $0 --no-wait --yes'
- Close the Cloud Shell prompt at the bottom of the portal.
Result: In this exercise, you removed the resources used in this lab.









Ulasan
Catat Ulasan